Theme: Advancement in botanical research
Plant Science & Physiology 2017

Welcome to the Plant Physiology and Pathology 2017 in Bangkok, Thailand! This will be an exciting event. The conference will have over 200 participants from 33 countries representing North and South America, Asia-Pacific and Middle East, Europe and UK. The conference will feature over 10 keynote speeches and 50 plenary lectures from world-renowned scientists, 15 interactive sessions, 3 workshops, and 10 exhibits, etc. There will be a wide range of topics that include crop physiology and biochemistry, epigenetics, system biology, frontier research in plant science, disease resistance mechanisms and control, regulation of plant growth and development, study of biofuel pathways, nitrogen utilization, plant biodiversity, and plant tissue culture. In addition to oral presentations, numerous posters and abstracts will be presented. Participants shall have good opportunity to interact with colleagues, peers, and biotech company’s representatives as well as take breaths of new discoveries and technology innovations.
The city of Bangkok, Thailand, is a good place of tourist attraction. Contrast to many cities of tourist attractions, Bangkok is a more relaxed place than many other places with inexpensive and easy public transport and welcoming residents. One can easily move smoothly and lightly between world-class boutiques and local markets before browsing the stalls that line the streets. Spiking up between the malls and tower blocks are the bell-shaped relic chambers of the Buddhist temples and wats that offer places of solace throughout the city. Well-known tourist attractions include tasting Thai food such as Thai home cooking, taking a city safari, cruising through Bangkok’s hidden klongs, cycling through Bangkok’s jungle, exploring Bangkok’s pastoral surroundings, and experiencing Bangkok at night with a local resident and many more…..
Sincerely,

ConferenceSeries Ltd Conferences invites all the participants from all over the world to attend '2nd International conference on Plant Science & Physiology' during June 26-27, 2017 in Bangkok, Thailand which includes prompt keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations and Exhibitions.
ConferenceSeries Ltd welcomes you to the International Conference on Plant Science & Physiology to be held from June 26-27, 2017 in Bangkok, Thailand. ConferenceSeries Ltd organizes 1000+ Global events inclusive of 300+ International Conferences every year across the globe with support from 1000 more International societies and Publishes 500+ leading-edge peer reviewed Open access journals which contains over 50000 Eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Plant Science and Physiology is the study of all fundamental chemical and physical process occurring in plant. It is a sub discipline of botany or plant biology concerned with the functioning or physiology of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), plant cell biology, plant genetics, biophysics and molecular biology. The conference expects the participation of experts from various cross disciplines like plant biology , plant science , plant physiology, plant pathology, botany, plant biotechnology, horticulture, forest science and those in the fields conducting plant and crop science related research.
Why to attend???
As we discussed before the importance of plants in human life is significant. Plants and plant products are essential for us. Food, energy, medicine and so many things we can get from plants. This conference seek to bring all such scientist, Noble Laureate, researcher, research scholar, students and people together who are involved in plant biology, plant science, forest science, soil science agricultural science field and provide them to discuss about their innovation, exchange ideas and interaction with each other.
Target Audience:
- Directors, Board Members, Presidents, Vice Presidents, Deans and Head of the Departments
- Plant Biology Researchers, Scientists, Faculties, Students
- Plant Science Associations and Societies
- Agricultural companies
- Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries
- Plant Biotechnology companies
- Drug Manufacturing Companies and Industries
- Laboratory Technicians
- Business Entrepreneurs and Industrialists
Track 1: Plant Physiology
Plant physiology is the study of all fundamental chemical and physical process occurring in plant. These are the sub discipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), crop physiology, plant cell biology, biophysics and plant stress physiology. Plant physiology seeks to understand all the aspects and manifestations of plant life. In agreement with the major characteristics of organisms, it is usually divided into three major parts: (1) the physiology of nutrition and metabolism, which deals with the uptake, transformations, and release of materials, and also their movement within and between the cells and organs of the plant; (2) the physiology of growth, development, and reproduction, which is concerned with these aspects of plant function; and (3) environmental physiology, which seeks to understand the manifold responses of plants to the environment. The part of environmental physiology which deals with effects of and adaptations to adverse conditions—and which is receiving increasing attention—is called stress physiology. Plant Biochemistry or phytochemistry is the study of chemical reaction occurring in plants.
Related conference:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; 6th International Conference on Genomics Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New exico;Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; International Society for Plant Pathology;
Track 2: Plant disease & Plant pathogens
Plant Pathology is defined as the study of diseases in plant that cause by the pathogens, the mechanisms by which this occurs, the interactions between these causal agents and the plant (effects on plant growth, yield and quality), and the methods of managing or controlling plant disease. It also interfaces knowledge from other scientific fields such as mycology, microbiology, virology, biochemistry, bio-informatics, etc. Plant Diseases caused by plant pathogens like fungi, bacteria, nematodes, viruses, parasitic flowering plants, abiotic factors of the environment including light, temperature, and atmospheric gases. Plant diseases are recognized by the symptoms (external or internal) produced by them or by sick appearance of the plant. The term plant disease signifies the condition of the plant due to disease or cause of the disease. Plant disease is mainly defined in terms of the damage caused to the plant or to its organ.
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture and Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat geneticsNovember 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK;
Track 3: Plant & Agricultural Biotechnology
Plant and Agricultural biotechnology are specific area of plant science involving the use of scientific tools and techniques, including genetic engineering, molecular markers, molecular diagnosis, vaccines, and tissue culture to modify living organisms: plant, animal and microorganism. Agricultural biotechnology is majorly used to alter the genome sequence of crops and those crops can be termed as transgenic or genetically modified crops. This helps to increase crop yield and good food quality. The agricultural biotechnology market has been classified based on applications into transgenic crops and synthetic biology-enabled products and tools. Agricultural biotechnology comprises Agriculture genetics and Plant breeding, Agronomy, Agricultural Extension, Agricultural engineering and technology, hybrid seed technology, Agricultural risk management, Modelling tools in agricultural DSS (Decision Support System). Plant breeding is the process of using two parent plants to create an “offspring” plant. It involves manipulation of plant species in order to create desired genotypes and phenotypes for specific purposes. Manipulation involves either controlled pollination, genetic engineering, or both, followed by artificial selection of progeny. Using conventional plant breeding technology agriculture productivity is increased.
5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture, June 27-29 2016, Cape Town, South Africa; 2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 31-November 02 2016, Baltimore, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; Poland; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 5th InternationalConference on Biodiversity, March 10-12 2016, Madrid, Spain; 2nd International Conference on Green Energy & Expo, November 28-30 2016, Chicago, USA; International Conference on Agriculture and Forestry, June 01-03 2016, Manila, Philippines; 18th International Conference on Agroforestry and Food Security, August 11-12 2016, Barcelona, Spain; 18th International Conference on Agroforestry and Agriculture, August 11-12, 2016, Barcelona, Spain; Ecological Farming Association Conference, January 20-23 2016, Pacific Grove, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic;
Tracks 4: Traditional medicine
Medicinal plants are important sources for pharmaceutical manufacturing. The Medicinal plants have been identified and used throughout human history. Supply chain management and value addition of MAPs Plants have the ability to synthesize a wide variety of chemical compounds that are used in cure various diseases. Mostly they are used in herbal therapies, tratidional medicine practioners. They are also which are used in making perfumes, in cooking, and in the food, pharmaceutical, and liquor industries. Many aromatic plants are species of the Lauraceae, Umbelliferae, Myrtaceae, and Labiatae families. In the USSR roses, geraniums, laurel, lavender, and rosemary are among the plants used in industry. Quality control standardization and certification of medicinal plants and herbal products is very important. Ginseng is perhaps the most widely recognized plant used in traditional medicine and now plays a major role in herbal health care. Through the ages, the root has been used in the treatment of loss of strength, hardened arteries, blood and bleeding disorders, and colitis, and to relieve the symptoms of aging, cancer, and senility.
Related conference:
Plant Genetics basically deals with heredity, especially the mechanisms of hereditary transmission and the variation of inherited characteristics among plant. Although there has been a revolution in the biological sciences in the past twenty years, there is still a great deal that remains to be discovered. The completion of the sequencing of the genomes of rice and some agriculturally and scientifically important plants (for example Physcomitrella patens) has increased the possibilities of plant genetic research immeasurably. Molecular biology is the study of biology and cell at a molecular level. It concerns itself with understanding the interactions between the various systems of a cell, including the interrelationship of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, protein structure and learning how these interactions are regulated. Biomolecules, gene expression, gene regulation, biochemical pathways are the part of this.
Related conference:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ;Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat geneticsNovember 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; 4th Plant Genomics Congress: Europe, May 9-10, 2016, London, UK;
Generation or reproduction is the natural process by which new "posterity" singular creatures are created from their "guardians". Generation is a key gimmick of all known life; every individual creature exists as the consequence of multiplication. The known routines for propagation are comprehensively gathered into two principle sorts: sexual and agamic. Plants have evolved different reproductive strategies for the continuation of their species. Plants have two types of reproduction system sexual and asexual. Plant sexual reproduction usually depends on pollinating agents, while asexual reproduction is independent of these agents. Flowers are often the showiest or most strongly-scented part of plants. With their bright colors, fragrances, and interesting shapes and sizes, flowers attract insects, birds, and animals to serve their pollination needs. Other plants pollinate via wind or water; still others self-pollinate.
Related conference:
Plant nutrition is the investigation of the compound components and aggravates that are important for plant development, and additionally of their outer supply and interior digestion system. In 1972, E. Epstein characterized two criteria for a component to be key for plant development: in its nonattendance the plant is unable to finish a typical life cycle or that the component is some piece of some fundamental plant constituent or metabolite. Most soil conditions over the world can furnish plants with sufficient sustenance and don't oblige manure for a complete life cycle. Plant nutrition is related to plant hormones. Plant hormones are the chemical which regulate or promote plant growth under some environmental condition.
Related conference:
Crop science is concerned with selection and improvement of crops. It includes research and development on production techniques, improving agriculture productivity, soil fertility, maintenance, protection, harvesting and storage aspects of post-harvest, pest management. Soil fertility is ability of soil to provide all essential plant nutrients in available forms and in a suitable balance, it support luxuriant growth of plants with very little human effort. It contains sufficient minerals, soil organic matter, and good soil structure and soil moisture retention. Soil fertility is of two type’s permanent and temporary fertility. Humans are depended on plants or crops for food, fibber and more recently for fuel. Crop production is deals with growing crops for use as food, fibre and other use and Crop productivity is the quantitative measure of crop yield in given measured area of field. The use of new crop varieties and the efficient application of agrochemicals, immensely contributed to increased plant productivity. Demand of crop production is rising because of increasing population. So the market value of crop is also increasing day by day.
Related conference:
Track 9: Agriculture & Horticulture
Agricultural science is the study of the science and management of biological systems like plant animal for the sustainable production of food and fibre. Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of medicinal plant, fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and non-food crops such as grass and ornamental trees and plants. It also includes plant conservation, landscape restoration, landscape and garden design, construction, and maintenance, and arboriculture. Horticulturists apply their knowledge, skills, and technologies used to grow intensively produced plants for human food and non-food uses and for personal or social needs. Their work involves plant propagation and cultivation with the aim of improving plant growth, yields, quality, nutritional value, and resistance to insects, diseases, and environmental stresses. They work as gardeners, growers, therapists, designers, and technical advisors in the food and non-food sectors of horticulture.
Track 10: Entrepreneurs Investment Meet
Importance & Scope:
Plant Physiology is a subdivision of botany or plant biology and it is the study of physical, chemical and biological functions of living plants, right from the from the whole plant down to the cellular level. It covers a wide range of scientific study of plant. It includes Plant morphology, molecular biology of plants, plant genetics, phytochemistry, plant pathology, and different genera of plants. Plant pathology dealing with basic, fundamental and advanced methods and discoveries includes essential plant pathology, it is an integration of many biological disciplines and bridges the basic and applied sciences. As a science, plant pathology encompasses the theory and general concepts of the nature and cause of disease, and yet it also involves disease control strategies, with the ultimate goal being reduction of damage to the quantity and quality of food and fiber essential for human existence.
Plant physiology & pathology has roots in plant biology , agriculture and plant physiology also has scope in agriculture fields, medicine, food production and textiles. It is the main source of food for human being. As well as we can get plant proteins, phytochemicals from plants, from medicinal plants some medicines are prepared and which can cure some fatal diseases. Form some recent study it is proved that plant antioxidant helps us to protect from free radical damage. By using Phytochemicals some cancer cell proliferation can be prevented at earlier stage. Beside that we can increase the nutrition value of plant by plant biotechnology and plant breeding. Now days green energy are used as non-conventional source of energy to reduce environmental pollution. So in human life plant physiology and plant oriented studies are very much important to sustain in this planet.
Why Thailand?
The current population in Thailand is 68,151,475, almost 27 million persons (39 percent of the total population) are involved in agriculture. The total area is approximately 514,000 square kilometers. Forty-one percent of the total land area is used for agricultural purposes, thirty-one percent is forest land and twenty-eight percent is unclassified land. Thailand is predominantly an agricultural country. About 11 percent of the gross domestic product is derived from agricultural sector. Agricultural products in Thailand have not been produced for their own consumption but also being a major source of income from exporting. The value of agricultural exports is increasing every year and still a major source of export earning. Currently agricultural exports constitute about 27 percent of the total export value. Thailand will maintain its status as a key Asian agricultural provider in the coming years, as the sector boasts strong export opportunities and government support, as well as an efficient food producing industry. Thai government is attempting to enhance agricultural productivity. By increasing productivity, it is essential to raise incomes and improves the living standard of the people. The sugar and livestock sectors hold promising growth stories. However, the government's interference in the market, especially in the rice sector, will hinder the competitive ness of Thai production compared to its Asian rivals. Rice production will face downward pressure as the government incentivises farmers to switch away from rice towards other crops, mainly sugarcane, in a bid to curb oversupply of rice. That said, Thailand will likely regain its status as the world's largest rice exporter in the coming years as production picks up aft er the drought recorded in 2015- 2016.
Conference Highlights:
Plant Physiology
Plant Pathology
Crop science
Agricultural & Plant Biotechnology
Plant Genetics & Genomics
Traditional medicines
Medicinal plants
Plant Stress biology
Ecology
Major Plant science Associations around the Globe
- American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB)
- Agricultural Science Society of Thailand(ASST)
- Australian Society of Plant Scientists (ASPS)
- Argentinean Society of Plant Physiology (SAFV)
- American Society of Agronomy (ASA)
- African Crop Science Society (ACSS)
- Brazilian Society of Plant Physiology (SBFV)
- Botanical Society of China (BSC)
- Canadian Society of Plant Biologists (CSPB)
- Chile’s National Network of Plant Biologists (CNNPB)
- Chinese Society of Plant Biology (CSPB)
- Crop Science Society of America (CSSA)
- Crop Science Society of China (CSSC)
- European Association for Research on Plant Breeding (EUCARPIA)
- European Plant Science Organisation (EPSO)
- Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology (FESPB)
- Genetics Society of China (GSC)
- International Society of Plant Pathology (ISPP)
- Indian Society of Plant Physiology (ISPP)
- International Crop Science Society (ICSS)
- International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS)
- Irish Plant Scientists' Association (IPSA)
- International Society for Plant Molecular Biology (ISPMB)
- Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology (JSPCMB)
- Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists (JSPP)
- Korean Society of Plant Biologists (KSPB)
- New Zealand Society of Plant Biologists (NZSPB)
- The Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology
- UK Plant Science Federation (UKPSF)
Agricultural & Plant Science Universities in Thailand:
- Kasetsart University
- Bangkok and Nakhon Pathom Maejo University
- Chiangmai, Phrae and Chumphon
- Chiang Mai University
- Chiangmai Khon Kaen University
- Khon Kaen Prince of Songkla University
- Songkla and Surat Thani King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
- Bangkok and Chumphon Ubon Ratchathani University
- Ubon Ratchathani Naresuan University
- Phitsanulok Silpakorn University
- Phetchaburi Suranaree University of Technology
- Nakhon Ratchasima Walailak University
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Thammasat University
- Pathum Thani Mahidol University,
- Kanchanaburi Private Universities
- Asian Institute of Technology
- Pathum Thani
Types and locations of edible plants found in 25 National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries in Thailand
|
General local edible plants |
169 |
|
Northeast |
76 |
|
West and South |
112 |
|
Southeast |
85 |
|
Central |
45 |
|
North |
117 |
|
Limestone mountains |
97 |
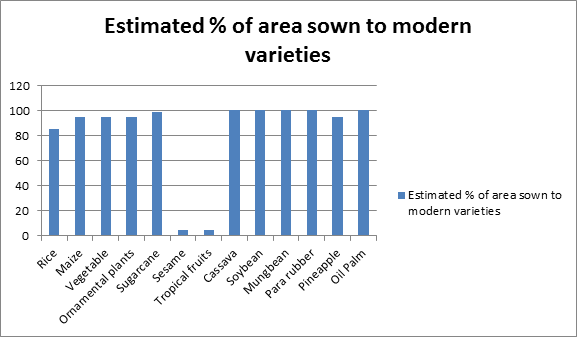
Major crops or cropping systems and percentage area sown to modern varieties:
Conference Highlights
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 26-27, 2017 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Plant Physiology & Pathology
- Journal of Plant Pathology & Microbiology
- Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by












































