Theme: New Horizon in Plant Science
Plant Physiology 2016
ConferenceSeries Ltd Conferences invites all the participants from all over the world to attend 'International Conference On Plant Physiology' during June 9-10, 2016 in Dallas, USA which includes prompt keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations and Exhibitions.
ConferenceSeries Ltd welcomes you to the International Conference on Plant Physiology to be held from June 9-10, 2016 in Dallas, USA. ConferenceSeries Ltd organizes 1000+ Global events inclusive of 300+ International Conferences every year across the globe with support from 1000 more International societies and Publishes 500+ leading-edge peer reviewed Open access journals which contains over 50000 Eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
The theme of Plant Physiology & Pathology -2016 is “New Horizon in Plant Science’’.Plant physiology is the study of all fundamental chemical and physical process occurring in plant. It is a sub discipline of botany or plant biology concerned with the functioning or physiology of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), plant cell biology, plant genetics, biophysics and molecular biology. The conference expects the participation of experts from various cross disciplines like plant biology , plant science , plant physiology, plant pathology, botany, plant biotechnology, horticulture and those in the fields conducting plant and crop science related research.
Why to attend???
As we discussed before the importance of plants in human life is significant. Plants and plant products are essential for us. Food, energy, medicine and so many things we can get from plants. This conference seek to bring all such scientist, Noble Laureate, researcher, research scholar, students and people together who are involved in plant biology, plant science, agricultural science field and provide them to discuss about their innovation, exchange ideas and interaction with each other.
Target Audience:
students, scientist, researchers, exhibitors from the related fields
Plant physiology conference offers comprehensive range of sessions that includes plant biology, plant biochemistry, plant genetics, plant pathology, plant biotechnology, agricultural biotechnology, plant derived chemicals or phytochemicals, molecular and cell biology of plant, pharmaceutical biotechnology and controlling environmental pollution by plant. There will be 11 tracks and 80 sub tracks for the conference.
Track 1: Plant Physiology and Plant Biochemistry
Plant physiology and plant biochemistry are the sub discipline of plant biology or plant science. Plant physiology is the study of all fundamental chemical and physical process occurring in plant. These are the sub discipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), crop physiology, plant cell biology, biophysics and plant stress physiology. Plant physiology seeks to understand all the aspects and manifestations of plant life. In agreement with the major characteristics of organisms, it is usually divided into three major parts: (1) the physiology of nutrition and metabolism, which deals with the uptake, transformations, and release of materials, and also their movement within and between the cells and organs of the plant; (2) the physiology of growth, development, and reproduction, which is concerned with these aspects of plant function; and (3) environmental physiology, which seeks to understand the manifold responses of plants to the environment. The part of environmental physiology which deals with effects of and adaptations to adverse conditions—and which is receiving increasing attention—is called stress physiology. Plant Biochemistry or phytochemistry is the study of chemical reaction occurring in plants.
The global market for ubiquitin proteasome research and development was estimated at nearly $2.9 billion in 2013. The market should total more than $5.5 billion by 2018, and have a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.2% from 2013 to 2018.
Related Conference:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; International Society for Plant Pathology;
Track 2: Plant Pathology & Weed science
Plant pathology is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by the infectious microorganisms like fungi, bacteria, viruses, viroid, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes, Ascomycetes and parasitic plants. These are called plant pathogens. Plant disease epidemiology is the study of disease in plant populations. Molecular Plant Pathology describes how pathogens cause disease, including analysis of the molecular signalling between plant, pathogens and genes. Molecular plant pathology can be exploited to control disease and thereby maximize crop yield. It covers the three main areas of plant pathology: how pathogens cause disease; (the molecular signalling that takes place between plant and pathogen); how plants resist disease (what is known about resistance genes, apoptosis, and systemic-acquired resistance). To protect the plant from plant pathogens, there is a new method called Gene Silencing used to form a transgenic plant, by gene silencing method expression of a gene can be switched off. Gene silencing is done by incorporating the DNA to be silenced into a form of DNA called heterochromatin that is already silent.
Weed control or weed management is the organic segment of vermin control, which endeavours to stop weeds, particularly poisonous or damaging weeds. Weed species are generally best controlled with post emergence translocate herbicides. Methods used to manage weeds include prevention, cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical.
According to the new market research report “Global Bacterial Biopesticides Market by Application (Seed Treatment, On Farm and Post-Harvest),by Type (Bacillus Thuringiensis, Bacillus Subtilis, Pseudomonas Fluorescens), by Crop Type, by Geography - Analysis and Forecast to 2019”, this market is estimated to grow from $1,438.6 million in 2014 to $2,697.6 million by 2019, at a CAGR of 13.4% from 2014 to 2019.’
Related Conferences:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture and Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK;
Track 3: Crop Production and its market analysis
Crop science is concerned with selection and improvement of crops. It includes research and development on production techniques, improving agriculture productivity, soil fertility, maintenance, protection, harvesting and storage aspects of post-harvest, pest management. Soil fertility is ability of soil to provide all essential plant nutrients in available forms and in a suitable balance, it support luxuriant growth of plants with very little human effort. It contains sufficient minerals, soil organic matter, and good soil structure and soil moisture retention. Soil fertility is of two type’s permanent and temporary fertility.
Humans are depended on plants or crops for food, fibber and more recently for fuel. Crop production is deals with growing crops for use as food, fibre and other use and Crop productivity is the quantitative measure of crop yield in given measured area of field. The use of new crop varieties and the efficient application of agrochemicals, immensely contributed to increased plant productivity. Demand of crop production is rising because of increasing population. So the market value of crop is also increasing day by day.
According to a new report from Pike Research, the increased production and consumption of biofuels will more than double the industry’s market value in the next decade. The cleantech market intelligence firm forecasts that the global market for biofuels will increase from $82.7 billion in 2011 to $185.3 billion by 2021.
The global biofertilizers market is projected to generate a value of $1,649.7 million, at a CAGR of 13.9%, by 2019.
The global market for biopesticides was valued at $1,796.56 Million in 2013 and is expected to reach $4,369.88 Million by 2019, growing at a CAGR of 16.0% from 2014 to 2019. North America dominated the global biopesticides market. Europe is expected to be the fastest growing market in the near future owing to the stringent regulation for pesticides and increasing demand from organic products.
Related conferences:
5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture, June 27-29, 2016, Cape Town, South Africa; 7th Global Summit on Agriculture & Horticulture, October 17-19 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; 6th Agriculture Industry and Machinary Congress, September 26-28, 2016, Miami, USA; 2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 31-November 02, 2016, Baltimore, USA; ISTA Seed Symposium, June 15-17 2016, Tallinn, Estonia; Combined Crops, Soils, Horticulture and Weeds Congress 2016, January 18-21 2016, Free State, Bloemfontein; 18th International Conference on Agronomy and Crop Sciences, September 15-16 2016, Rome, Italy; 7th International Crop Science Congress, August 14-19 2016, Beijing China. Crop Science Society of America;
Track 4: Agricultural Biotechnology
Agricultural biotechnology is a specific area of agricultural science involving the use of scientific tools and techniques, including genetic engineering, molecular markers, molecular diagnosis, vaccines, and tissue culture to modify living organisms: plant, animal and microorganism. Agricultural biotechnology is majorly used to alter the genome sequence of crops and those crops can be termed as transgenic or genetically modified crops. This helps to increase crop yield and good food quality. The agricultural biotechnology market has been classified based on applications into transgenic crops and synthetic biology-enabled products and tools. Agricultural biotechnology comprises Agriculture genetics and Plant breeding, Agronomy , Agricultural Extension, Agricultural engineering and technology, hybrid seed technology, Agricultural risk management, Modelling tools in agricultural DSS (Decision Support System). Plant breeding is the process of using two parent plants to create an “offspring” plant. It involves manipulation of plant species in order to create desired genotypes and phenotypes for specific purposes. Manipulation involves either controlled pollination, genetic engineering, or both, followed by artificial selection of progeny. Using conventional plant breeding technology agriculture productivity is increased.
According to a new market study published by Transparency Market Research (TMR), titled “Agricultural Biotechnology Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends and Forecast, 2013 - 2019”, the global agricultural biotechnology market was worth US$15,300 million in 2012 and is expected to be worth US$28,694.1 million by 2019, expanding at a 9.5% CAGR from 2013 to 2019.Growing population worldwide has led to demand for genetically modified (GM)crops for high yield, which is one of the primary drivers for the growth of the agricultural biotechnology market. Increasing demand for biofuels due to depleting reserves of conventional fuels is further boosting the agricultural biotechnology market.
Related conferences:
5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture, June 27-29 2016, Cape Town, South Africa; 2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 31-November 02 2016, Baltimore, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; Poland; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 5th International Conference on Biodiversity, March 10-12 2016, Madrid, Spain; 2nd International Conference on Green Energy & Expo, November 28-30 2016, Chicago, USA; International Conference on Agriculture and Forestry, June 01-03 2016, Manila, Philippines; 18th International Conference on Agroforestry and Food Security, August 11-12 2016, Barcelona, Spain; 18th International Conference on Agroforestry and Agriculture, August 11-12, 2016, Barcelona, Spain; Ecological Farming Association Conference, January 20-23 2016, Pacific Grove, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic;
Track 5: Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Plants have been used for therapeutic, cosmetic, nutritional, and beautification purposes since ancient times and humanity of all civilizations and culture are familiar with their usage. Herbs have been used prevalently as home remedies to treat diseases seasonal like cough, cold, stomach-ache etc. in several countries of Asia, Africa and Europe. Medicinal plant has the ability to synthesis wide variety of chemical which are used to produce natural medicine. At least 12,000 such chemical compounds are isolated from medicinal plants. Among them 122 compounds are used in modern medicine, which were derived from the medicinal plant sources. There are also some medicinal fungi or medicinal mushrooms which produce medically important chemicals like antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol inhibitors, psychoactive drugs, immunosuppressant and even fungicides also. Aromatic plants are those which produce and exude Aromatic substances, which are used in making perfumes, in cooking, and in the food, pharmaceutical, and liquor industries. Many aromatic plants are species of the Lauraceae, Umbelliferae, Myrtaceae, and Labiatae families. Many of them are also used for medicinal purposes. Aromatic plants are from a numerically large group of economically important plants.
The report based on “Nutraceutical Ingredients Market – Global Industry Analysis, Market Size, Share, Growth and Forecast, 2007 – 2017,” elaborated by Transparency Market Research is expected to be worth USD 20.8 billion in 2012 and is further expected to reach USD 29.5 billion in 2017, growing at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2012 to 2017. The nutraceutical are derived from phytochemicals.
Related Conferences:
6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; 8th International Conference on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems, March 13-15, 2017 London, UK; International Conference and Exhibition on Marine Drugs and Natural Products , July 28-30, 2016 Melbourne, Australia; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 2nd International Conference on Green Energy & Expo, November 28-30 2016, Chicago, USA; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; 9th Conference on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of Southeast European Countries May 26-29, 2016, Plovdiv, Bulgaria; 9th Joint Natural Products Conference, July 24-27, 2016, Copenhagen, Denmark; American Herbal Products Association; International Herb Association;
Track6: Plant Ecology & Agro- diversity
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms and environments, the interactions of organisms with one another. Plant ecology is the study of plant ecosystem, from plant ecology we can study the distribution and abundance of plants, the interactions among and between plants and other organisms and the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants. Agro-biodiversity is a part of plant biodiversity which is the result of natural selection processes and the careful selection and inventive developments of farmers, herders and fishers over millennia.
Related Conference:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; Ecological Society of America;
Track7: Plant Genetics and Plant Molecular biology
Plant Genetics basically deals with heredity, especially the mechanisms of hereditary transmission and the variation of inherited characteristics among plant. Although there has been a revolution in the biological sciences in the past twenty years, there is still a great deal that remains to be discovered. The completion of the sequencing of the genomes of rice and some agriculturally and scientifically important plants (for example Physcomitrella patens) has increased the possibilities of plant genetic research immeasurably. Molecular biology is the study of biology and cell at a molecular level. It concerns itself with understanding the interactions between the various systems of a cell, including the interrelationship of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, protein structure and learning how these interactions are regulated. Biomolecules, gene expression, gene regulation, biochemical pathways are the part of this.
Related Conferences:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting August 4-7, 2016, Sante Fe, New Mexico; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; 4th Plant Genomics Congress: Europe, May 9-10, 2016, London, UK;
Track 8: Plant Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the technical application to modify any organism by addition or deletion of genes and to make improved and modified organism. There are various modern techniques to develop genetically modify plants, genetically engineered crops. By r-DNA technology we can produce a recombinant DNA and insert it in to a vector thus genetically modified crops are produced. Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms. Epigenetics is the interchanging between the heredity and the environment through molecular mechanisms (DNA methylation, gene silencing, fluorescent in situ hybridization). Plant Molecular farming is a part of the plant biotechnology industry that involves the process of genetically engineering plants so that they can produce various types of therapeutic proteins and molecules such as peptides and secondary metabolites. These genetically modified proteins and molecules can then be harvested and used to produce pharmaceuticals. Plant Biotechnology is emerging in the field of medicine interfacing biotechnology and bioinformatics; the molecular characterization of medicinal plants; molecular farming; and leads from chemistry, nanotechnology etc.
Related Conferences:
5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture, June 27-29 2016, Cape Town, South Africa; 7th Global Summit on Agriculture & Horticulture, October 17-19 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; 6th Agriculture Industry and Machinary Congress, September 26-28 2016 Miami, USA; 2nd International Conference on Green Energy & Expo, November 28-30 2016, Chicago, USA; 4th International Conference on Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, October 20-21 2016, Houston, USA; 10th Asia Pacific Biotech Congress July 25-27, 2016, Bangkok, Thailand; 18th International Conference on Agriculture and Environmental Systems, March 01-02 2016, Miami, USA; International Conference on Agriculture and Food Engineering, May 11-13 2016, Copenhagen, Denmark; 2nd International Conference on Biotechnology and Agricultural Engineering, April 08-09 2016, Tokyo, Japan. Plant Biotech 2016, June 19-21, 2016, Ontario, Canada; 4th Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA; The Canadian Society of Plant Biologists; Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology;
Track9: Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are plant derived chemical compounds. Antioxidants, Primary and secondary metabolite, atropine, and some antibiotics derived from plant, all are phytochemicals. There are thousands of phytochemicals are found in vegetables, fruits, beans, whole grains, nuts and seeds. Basically they don’t have any nutrition value for human beings but they have some other properties like antibacterial properties, hormonal and enzymatic properties and antioxidant effect. Antioxidants also prevent the free radical damage in cancer and other heart disease. Plant basically produces these chemicals for protect them from any microbial infection. There is a lot of use of phytochemicals in human life. Example of some phytochemicals are Alkaloids, Monoterpenes, Anthocyanin, Organosulfides, Carotenoids, Coumestans, Flavonoids, Hydroxycinnamic acid, Isoflavones, Lignin, Monophenols, Phenolic acid, Phytosterols, Saponins, Stylbenes, Triterpenoids and Xanthophylls. Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. We can prevent it in early stages by Chemo/radio therapy or some other technique. But some time it becomes dangerous to the patient’s life. Instead of these phytochemical can be used to prevent Environmental carcinogenesis, Inflammation, Tumour angiogenesis, Metastasis, Apoptosis, Cancer cell metabolism. There are number of phytochemicals are there some of them are curcumin (derived from turmeric), apigenin(derived from parsley), Crocetin (derived from saffron), cyanidins (from grapes), Indole-3-carbinol (I3C) ( from Brassica vegetables), Epigallocatechin gallate (from green tea), Fisetin (from strawberries, apples), Genistein (from soybean), Gingerol (from gingers), Kaempferol (from tea, broccoli, grapefruit) and many others.
The Europe phytochemicals & plant extracts market is estimated to grow from $833.7 million in 2014 to $1.25 billion by 2019, at a CAGR of 8.4% during the period under consideration.
Related Conference:
2nd Global Summit on Plant Science, October 06-08, 2016 Crowne Plaza, Heathrow, London, UK; 8th International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems, March 13-15, 2017 London, UK; 5th International Conference on Agriculture & Horticulture June 27-29, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa ; Plant Genomics Congress September 12-13, 2016 Philadelphia, USA; 6th International Conference on Genomics & Pharmacogenomics September 22-24, 2016 Berlin, Germany; International Conference on Green Energy & Expo November 28-30, 2016 Atlanta, USA; Plant Biology 2016 July 9-13 Austin, Texas; 5th Pan American Plants and Bio Energy Meeting Sante Fe, New Mexico, August 4-7, 2016; Plant Biology Europe: EPSO/FESPB 2016 Congress June 26-30, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic; WISP Course on wheat genetics November 21-23. 2016 John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK; International Conference and Exhibition on Marine Drugs and Natural Products , July 28-30, 2016 Melbourne, Australia
Track 10: Mycology & Phycology
The term mycology and phycology both are derived from Greek word “mykes” and “phykos” accordingly. Mycology basically deals with the study of fungi and phycology is the study of algae. Fungi inhabit almost every niche in the environment and humans are exposed to these organisms in various fields of life. Many fungi are useful in medicine and industry. Mycological research has led to the development of such antibiotic drugs as penicillin, streptomycin, and tetracycline. Mycology also has important applications in the dairy, wine, and baking industries and in the production of dyes and inks. The fungi and algae both play an important role in ecosystem.
Related Conferences:
International conference on Mycology, September 12-14, 2016 San Antonio, USA; International Conference on Water Microbiology & Novel Technologies, July 18-20, 2016 Chicago, USA; International Conference on Microbial Physiology and Genomics | September 29-20, 2016 London, UK; 2nd World Congress on Beneficial Microbes, September 22-24, 2016 Phoenix, USA; 2nd International Congress and Expo on Biofuels & Bioenergy August 29-31, 2016 Sao Paulo, Brazil; 12th International Verticillium Symposium, October 6-9, 2016, Ljubljana, Slovenia. 18th Congress of European Mycologists, September 16-21, 2017, Warsaw and Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland; 22nd International Seaweed Symposium, June 19-24, 2016, Copenhagen, Denmark; North American Mycological Association; Phycological Society of America;
Track 11: Entrepreneurs Investment Meet
Importance & Scope:
Plant Physiology is a subdivision of botany or plant biology and it is the study of physical, chemical and biological functions of living plants, right from the from the whole plant down to the cellular level. It covers a wide range of scientific study of plant. It includes Plant morphology, molecular biology of plants, plant genetics, phytochemistry, plant pathology, and different genera of plants.
Plant pathology dealing with basic, fundamental and advanced methods and discoveries includes essential plant pathology, it is an integration of many biological disciplines and bridges the basic and applied sciences. As a science, plant pathology encompasses the theory and general concepts of the nature and cause of disease, and yet it also involves disease control strategies, with the ultimate goal being reduction of damage to the quantity and quality of food and fiber essential for human existence.
Plant physiology has roots in plant biology , agriculture and plant physiology also has scope in agriculture fields, medicine, food production and textiles. It is the main source of food for human being. As well as we can get plant proteins, phytochemicals from plants, from medicinal plants some medicines are prepared and which can cure some fatal diseases. Form some recent study it is proved that plant antioxidant helps us to protect from free radical damage. By using Phytochemicals some cancer cell proliferation can be prevented at earlier stage. Beside that we can increase the nutrition value of plant by plant biotechnology and plant breeding. Now days green energy are used as non-conventional source of energy to reduce environmental pollution. So in human life plant physiology and plant oriented studies are very much important to sustain in this planet.
Why Dallas?
As the ninth-largest city and part of the fourth-largest metropolitan area in the nation, Dallas covers approximately 343 square miles and has a population of 1,241,162. The ultra modern and sophisticated city attracts worldwide travellers, making the area the No. 1 visitor and leisure destination in Texas.
Dallas is centrally located and within a four-hour flight from most North American destinations. DFW International Airport is the world's fourth busiest airport, offering nearly 1,750 flights per day and providing non-stop service to 145 domestic and 47 international destinations worldwide annually. In addition, Dallas Love Field Airport is conveniently located 10 minutes from downtown. Once here, visitors can ride DART, one of the fastest-growing light rail systems in the nation or the historic, free McKinney Avenue Trolley from the Dallas Arts District throughout the Uptown area with its restaurants, pubs, boutique hotels and shops.
There are many visitor places in Dallas. Like, AT&T Performing Arts Center, Perot Museum of Nature and Science, Cotton Bowl, Dallas Museum of Art, George W. Bush Presidential Center, The Nasher Sculpture Center, Dallas Zoo, Klyde Warren Park, Dallas Arboretum and Botanical Garden, Dealey Plaza, Sixth Floor Museum at Dealey Plaza, Texas School Book Depository, Morton H. Meyerson Symphony Center, Southern Methodist University, Dallas Baptist University, Fair Park, Dallas World Aquarium, Victory Park, American Airlines Center, Reunion Tower, Margaret Hunt Hill Bridge, Texas Theatre etc.
Conference Highlights:
Plant Biochemistry and Plant Physiology
Plant Pathology and Weed Science
Crop production and market value
Agricultural Biotechnology
Plant Genetics
Phytochemicals
Medicinal plants
Plant Biotechnology
Mycology and Phycology
Major Plant science Associations around the Globe
American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB)
Australian Society of Plant Scientists (ASPS)
Argentinean Society of Plant Physiology (SAFV)
American Society of Agronomy (ASA)
African Crop Science Society (ACSS)
Brazilian Society of Plant Physiology (SBFV)
Botanical Society of China (BSC)
Canadian Society of Plant Biologists (CSPB)
Chile’s National Network of Plant Biologists (CNNPB)
Chinese Society of Plant Biology (CSPB)
Crop Science Society of America (CSSA)
Crop Science Society of China (CSSC)
European Association for Research on Plant Breeding (EUCARPIA)
European Plant Science Organisation (EPSO)
Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology (FESPB)
Genetics Society of China (GSC)
International Society of Plant Pathology (ISPP)
Indian Society of Plant Physiology (ISPP)
International Crop Science Society (ICSS)
International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS)
Irish Plant Scientists' Association (IPSA)
International Society for Plant Molecular Biology (ISPMB)
Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology (JSPCMB)
Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists (JSPP)
Korean Society of Plant Biologists (KSPB)
New Zealand Society of Plant Biologists (NZSPB)
The Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology
UK Plant Science Federation (UKPSF)
Global Market values:
Oregon's farm acreage totaled 16.3 million in 2012, with 35,439 farms and 59,237 farm operators. Of these, 39 percent were women farm operators. These results and more are available from the U.S. Department of Agriculture's report, 2012 Census of Agriculture. The purpose of the census of agriculture is to account for "any place from which $1,000 or more of agricultural products were produced and sold, or normally would have been sold, during the census year." Oregon agricultural product sales totaled $4.9 billion in 2012 and ranged from a high of $593 million in Marion County to $5.5 million in Lincoln County.
Ref: https://www.qualityinfo.org/-/down-on-the-farm-2012-census-of-agriculture-for-oregon
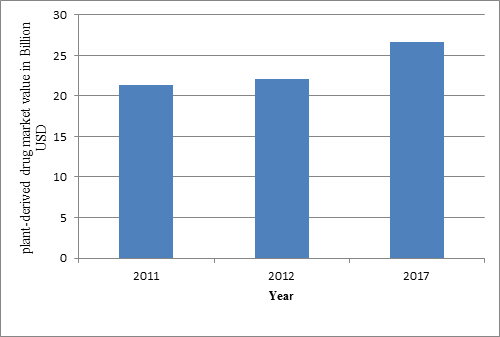
According to the new report from BCC Research, the global market for botanical and plant-derived drugs was valued at $23.2 billion in 2013 and $24.4 billion in 2014. This total market is expected to reach $25.6 billion in 2015 and nearly $35.4 billion in 2020, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2015 to 2020.
Ref: http://www.virtual-strategy.com/2015/09/02/plant-derived-compounds-poised-assume-greater-role-global-drug-markets-according-bcc-rese#ixzz3lu9TBnoI
Browse 71 market data tables and 96 figures spread through 196 pages and in-depth TOC on “Transgenic Seeds Market by Trait (Herbicide Tolerance, Insecticide Resistance), Crops (Corn, Soybean, Cotton, Canola, others), and by Region - Global Trends & Forecast to 2020"
Ref: http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/transgenic-seeds-market-63068971.html
Value of crops in Dallas, USA
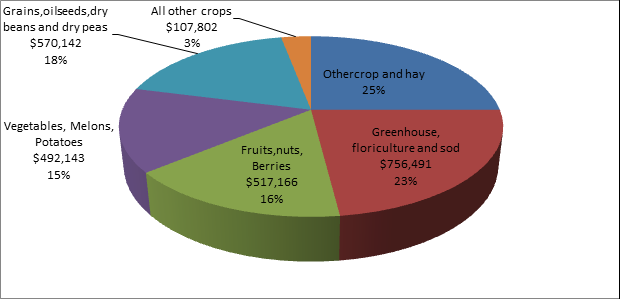
Ref: Down on the Farm - 2012 Census of Agriculture for Oregon
International Trade of New GM crops
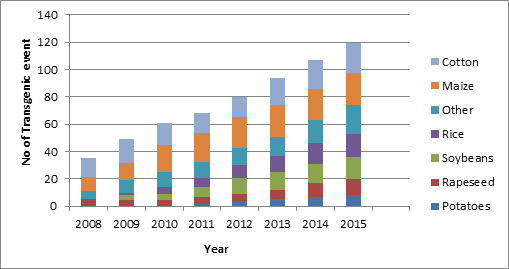
Ref: International trade and the global pipeline of new GM crops
URL- http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v28/n1/full/nbt0110-23b.html
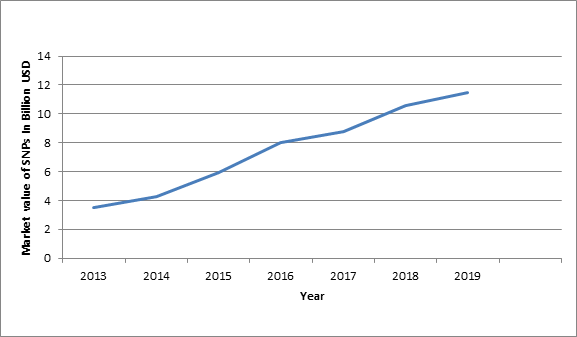
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Global Market value
Global agrochemical market value
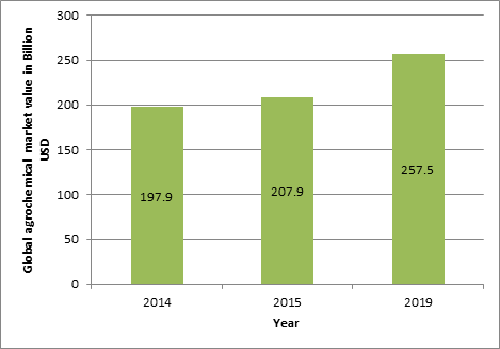
Ref: http://www.marketresearch.com/BCC-Research-v374/Global-Agrochemicals-8895289/
The global plant-derived drug market value
Conference Highlights
- Plant Physiology and Plant Biochemistry
- Plant Pathology & Weed science
- Crop Production and Market analysis
- Agricultural science and agricultural biotechnology
- Medicinal Plants
- Plant Ecology & Agro- diversity
- Plant Genetics and molecular biology of plant
- Plant Biotechnology and Tissue culture
- Phytochemicals
- Mycology & Phycology
- Entrepreneurs Investment Meet
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 09-10, 2016 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Plant Pathology & Microbiology
- Journal of Plant Physiology & Pathology
- Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by













